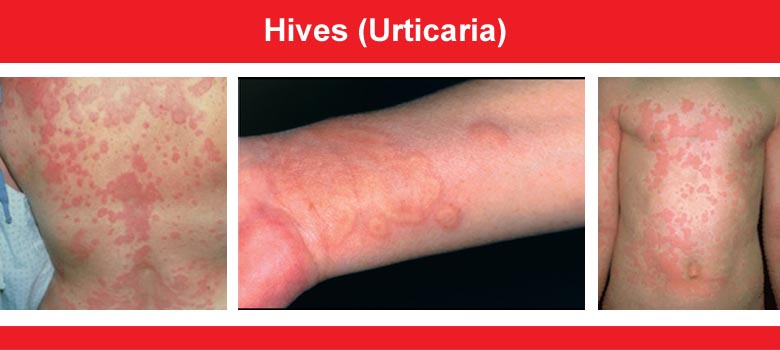
Urticaria, also known as hives, is an outbreak of swollen, pale red bumps or plaques on the skin that appear suddenly -- either as a result of the body's reaction to certain allergens or for unknown reasons. Hives usually cause itching, but may also burn or sting. They can appear anywhere on the body, including the face, lips, tongue, throat or ears. Hives vary in size and may join together to form larger areas known as plaques. They can last for hours, or up to one day before fading.
Causes of hives
Hives are often triggered by an allergic reaction in which the body releases histamine and other chemicals in the bloodstream that cause itching and swelling. Most common triggers include:
- Foods: fruits (citrus fruits), milk, eggs, nuts, fish and shellfish.
- Medicines
- Insect bites
- Animal dander (especially cats)
- Pollen
- Allergy shots
Hives may also develop as a result of
- Stress
- Infections
- Exercise
- Exposure to sun, cold, heat or water
- Some illnesses – lupus, thyroid disease
- Excessive perspiration
- Scratching the skin
Types of hives
- Acute urticaria Hives lasting less than six weeks. The most common causes are certain foods, medications, or infections. Insect bites and internal disease may also be responsible.Drugs that can cause hives and angioedema include aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen, high blood pressure drugs or painkillers such as codeine.
- Chronic urticaria and angioedema Hives lasting more than six weeks. The cause of this type of hives is usually more difficult to identify than those causing acute urticaria. For most people with chronic urticaria, the cause is impossible to determine. In some cases, though, the cause may be thyroid disease, hepatitis, infection, or cancer.Chronic urticaria and angioedema can affect other internal organs such as the lungs, muscles, and gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms include muscle soreness, shortness of breath, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Physical urticaria Hives caused by direct physical stimulation of the skin -- for example, cold, heat, sun exposure, vibration, pressure, sweating, and exercise. The hives usually occur right where the skin was stimulated and rarely appear elsewhere. Most of the hives appear within one hour after exposure.
- Dermatographism This is a common form of physical urticaria where hives form after firmly stroking or scratching the skin. These hives can also occur along with other forms of urticaria.
How lesions of urticaria starts
- Starts as red erythematous macules.
- Soon paleoedematous wheals develop.
- Irregular, asymmetrical.
- Velvetty to touch.
- Erythema well defined, fades on pressure.
- Subside within few hours without leaving any trace.
- Dermographism positive.
- Wheals develop along line of scratching or pressure.
If hives or angioedema occur with any of the following symptoms, contact your doctor right away
- Dizziness
- Wheezing
- Difficulty breathing
- Tightness in the chest
- Swelling of the tongue, lips, or face
COMPLICATIONS
- Angioneurotic oedema.
- Onset: sudden.
- Swelling of skin, mucous membranes.
- Common sites involved: eyelids, tongue, lips, glottis, genitalia, trunk, hands, feet.
- Wheals large, extensive.
- Lasts from few hours to few days.
General management of urticaria
- Reassurance.
- Identify and eliminate offending agent.
- Correct underlying cause.
- Avoid precipitating causes.
- During acute attack:
- Simple, bland diet.
- Avoid tea, coffee, alcohol.
Our treatment for hives
Conventional medicines such as anti-histamines alleviate symptoms but the root cause still remains. Homeopathy and ayurveda relieves the rash and itching and also eliminates the underlying cause. Homeopathic medicines are quite effective in the treatment of stress, grief or anger that often trigger bouts of hives. We have observed that chronic hives in many patients are associated with a bacterial, parasitic or fungal infections (staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus species, toxoplasma gondii, candida albicans). Once the infection is cured , hives stop coming back.

